Pain under your heel is caused by plantar fasciitis. Treatment may speed up recovery. Treatment includes manual therapy, good footwear, heel pads, painkillers, and exercises. A steroid injection or other treatments may be used in more severe cases.
What is plantar fasciitis?
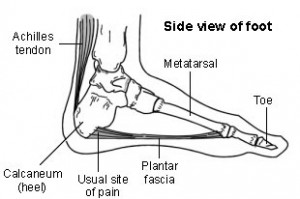
Plantar fasciitis means inflammation of your plantar fascia. Your plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue (like a ligament) that stretches from your heel to your middle foot bones. It supports the arch of your foot and also acts as a shock-absorber in your foot.
What causes plantar fasciitis?
Repeated small injuries to the fascia (with or without inflammation) are thought to be the cause of plantar fasciitis. The injury is usually near to where the plantar fascia attaches to your heel bone.
You are more likely to injure your plantar fascia in certain situations. For example:
- If you are on your feet for a lot of the time, or if you do lots of walking, running, standing, etc, when you are not used to it. Also, people with a sedentary lifestyle are more prone to plantar fasciitis.
- If you have recently started exercising on a different surface – for example, running on the road instead of a track.
- If you have been wearing shoes with poor cushioning or poor arch support.
- If you are overweight – this will put extra strain on your heel.
- If there is overuse or sudden stretching of your sole. For example: athletes who increase running intensity or distance; poor technique starting ‘off the blocks’, etc.
- If you have a tight Achilles tendon (the big tendon at the bottom of your calf muscles above your heel). This can affect your ability to flex your ankle and make you more likely to damage your plantar fascia.
Plantar fasciitis may be confused with ‘Policeman’s heel’, but they are different. Policeman’s heel is plantar calcaneal bursitis – inflammation of the sack of fluid (bursa) under the heel bone. This is not as common as plantar fasciitis.
Often there is no apparent cause for plantar fasciitis, particularly in older people. A common wrong belief is that the pain is due to a bony growth or ‘spur’ coming from the heel bone (calcaneum). Many people have a bony spur of the heel bone but not everyone with this gets plantar fasciitis.
How common is plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is common. Around 1 in 10 people will get plantar fasciitis at some time in their life. It is most common in people between the ages of 40 to 60 years. However, it can occur at any age. It is twice as common in women as it is in men. It is also common in athletes.
What are the symptoms of plantar fasciitis?
Pain is the main symptom. This can be anywhere on the underside of your heel. However, commonly, one spot is found as the main source of pain. This is often about 4 cm forward from your heel, and may be tender to touch.
The pain is often worst when you take your first steps on getting up in the morning, or after long periods of rest where no weight is placed on your foot. Gentle exercise may ease things a little as the day goes by, but a long walk or being on your feet for a long time often makes the pain worse. Resting your foot usually eases the pain.
Sudden stretching of the sole of your foot may make the pain worse – for example, walking up stairs or on tiptoes. You may limp because of pain. Some people have plantar fasciitis in both feet at the same time.
How is plantar fasciitis diagnosed?
Your medical professional can usually diagnose plantar fasciitis just by talking to you and examining your feet. Rarely, tests are needed if the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out other possible causes of heel pain. These can include X-rays of the heel or an ultrasound scan of the fascia. An ultrasound scan usually shows thickening and swelling of the fascia in plantar fasciitis.
What is the initial treatment for plantar fasciitis?
Usually, the pain will ease in time. ‘Fascia’ tissue, like ‘ligament’ tissue, heals quite slowly. It may take several months or more to go. However, the following treatments may help to speed recovery. A combination of different treatments may help. Collectively, these initial treatments are known as ‘conservative’ treatments for plantar fasciitis.
Manual Therapy
Frictioning and dry needling the plantar fascia. Stretching the Achilles tendon and calf muscles. Assessing foot mechanics to make sure that everything is in working order.
Rest your foot
This should be done as much as possible. Avoid running, excess walking or standing, and undue stretching of your sole. Gentle walking and exercises described below are fine.
Footwear
Do not walk barefoot on hard surfaces. Choose shoes with cushioned heels and a good arch support. A laced sports shoe rather than an open sandal is probably best. Avoid old or worn shoes that may not give a good cushion to your heel.
Heel pads and arch supports
You can buy various pads and shoe inserts to cushion the heel and support the arch of your foot. These work best if you put them in your shoes at all times. The aim is to raise your heel by about 1 cm. If your heel is tender, cut a small hole in the heel pad at the site of the tender spot. This means that the tender part of your heel will not touch anything inside your shoe. Place the inserts/pads in both shoes, even if you only have pain in one foot.
Pain relief
Painkillers such as paracetamol will often ease the pain. Sometimes anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen are useful. These are painkillers but also reduce inflammation and may work better than ordinary painkillers. Some people find that rubbing a cream or gel that contains an anti-inflammatory medicine on to their heel is helpful.
An ice pack (such as a bag of frozen peas wrapped in a tea towel) held to your foot for 15-20 minutes may also help to relieve pain.
Exercises
Regular, gentle stretching of your Achilles tendon and plantar fascia may help to ease your symptoms. This is because most people with plantar fasciitis have a slight tightness of their Achilles tendon. If this is the case, it tends to pull at the back of your heel and has a knock-on effect of keeping your plantar fascia tight. Also, when you are asleep overnight, your plantar fascia tends to tighten up (which is why it is usually most painful first thing in the morning). The aim of these exercises is to loosen up the tendons and fascia gently above and below your heel. Your medical professional will be able to prescribe an exercise regime.
Are there any other treatments?
If the above treatments are not helping to relieve your symptoms, or if you are someone such as an athlete who needs a quick recovery, other treatments are available. There is no one specific treatment that appears to stand out as the best.
Steroid injections
A steroid (cortisone) injection is sometimes tried if your pain remains bad despite the above ‘conservative’ measures. It may relieve the pain in some people for several weeks but does not always cure the problem. It is not always successful and may be sore to have done. Steroids work by reducing inflammation. Sometimes two or three injections are tried over a period of weeks if the first is not successful. Steroid injections do carry some risks, including (rarely) tearing (rupture) of the plantar fascia.
Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy
In extracorporeal shock-wave therapy, a machine is used to deliver high-energy sound waves through your skin to the painful area on your foot. It is not known exactly how it works, but it is thought that it might stimulate healing of your plantar fascia. One or more sessions of treatment may be needed.
This procedure appears to be safe but it is uncertain how well it works. This is mostly because of a lack of large, well-designed clinical trials. You should have a full discussion with your medical professional about the potential benefits and risks.
Surgery
This may be considered in very difficult cases. Surgery is usually only advised if your pain has not eased after 12 months despite other treatments. The operation involves separating your plantar fascia from where it connects to the bone; this is called a plantar fascia release. It may also involve removal of a spur on the calcaneum if one is present. Surgery is not always successful. It can cause complications in some people so it should be considered as a last resort. Complications may include infection, increased pain, injury to nearby nerves, or rupture of the plantar fascia.
What is the outlook (prognosis) for plantar fasciitis?
Most people have completely recovered from an episode of plantar fasciitis within a year. However, some of the treatments described above may help to speed up your recovery.
Can plantar fasciitis be prevented?
There are certain things that you can do to try to prevent plantar fasciitis, especially if you have had it before. These include:
- Regularly changing training shoes used for running or walking.
- Wearing shoes with good cushioning in the heels and good arch support.
- Losing weight if you are overweight.
- Regularly stretching the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, especially before exercise.
- Avoiding exercising on hard surfaces.
